Mediplus Pharma is presenting posters at Society for Investigative Dermatology(SID)annual meeting 2022
Mediplus Pharma, Inc. (CEO: Kenji Ito, Head Office: Shibuya-ku, Tokyo,JAPAN) made a scientific presentation at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology (May 18-21, 2022, Portland, USA), which is considered the world’s highest-level society in dermatological research.
Title:Novel glycerin compounds improve skin health
Digest
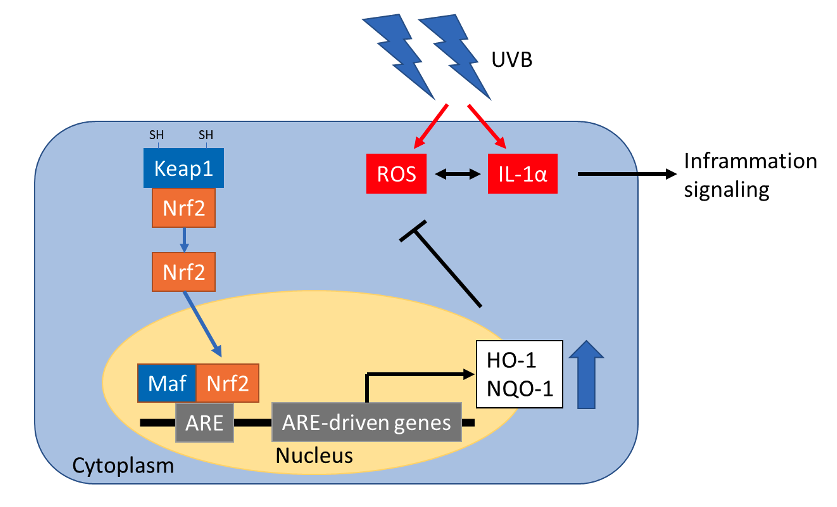
Novel glycerin compounds (NGCs) were developed which generated new reaction products. NGCs have been reported to exhibit various biological effects. This study is aimed to evaluate the effects of NGCs on skin homeostasis by investigating antioxidant activity and barrier functions. NGC enhanced expression of HO-1, NQO-1 mRNA and GSH protein in a concentration-dependent manner from 20 ppm after 24 h of stimulation. These results imply that the oxidative property of NGCs activates Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) transcription factor, which is a biological defense sensor, and induces the expression of antioxidant factors. It was strongly suggested that their hormesis effect would be working protectively for the skin. Mild oxidative stimulation of NGCs could lead to healthy skin through their hormesis effect on antioxidant activity and barrier functions.

Background
Novel glycerin compounds (NGCs) were developed which generated new reaction products. NGCs have been reported to exhibit various biological effects. In addition to their deodorizing, disinfecting and antiviral effects, NGCs were found to increase type I collagen production and inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion.
Purpose
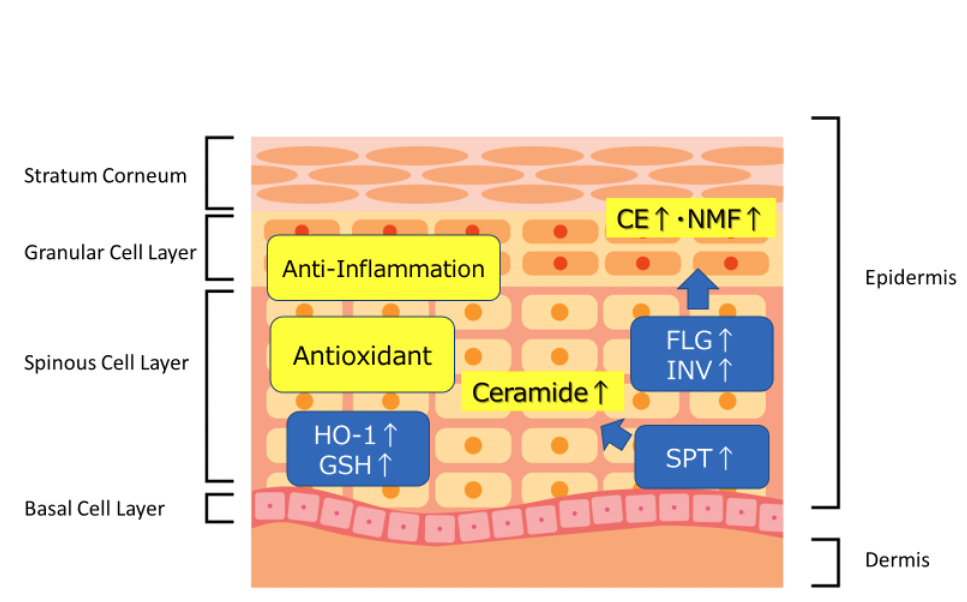
This study is aimed to evaluate the effects of NGCs on skin homeostasis by investigating antioxidant activity and barrier functions.
Method
In this study, in order to clarify the effects of NGCs on normal human skin, we quantified the mRNA gene expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and DAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO-1) as antioxidant factors by PR-PCR and the protein content of intracellular glutathione (GSH) using a culture system of normal human epidermal keratinocyte. Moreover, gene expression of factors related to skin barrier functions (involucrin (INV), filaggrin (FLG), and serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT)) was examined to clarify the effects of NGCs on epidermal cell differentiation.
Results
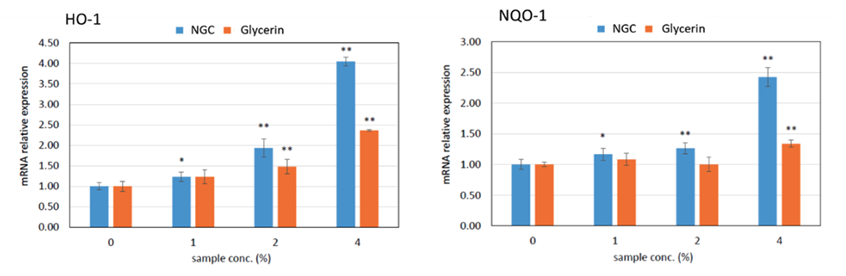
NGC enhanced expression of HO-1, NQO-1 mRNA and GSH protein in a concentration-dependent manner from 20 ppm after 24 h of stimulation. These results imply that the oxidative property of NGCs activates Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) transcription factor, which is a biological defense sensor, and induces the expression of antioxidant factors. It was strongly suggested that their hormesis effect would be working protectively for the skin.
Conlusion